By Hrishikesh Sathawane, Director of Product Planning, Samsung and Mike Allison, Sr. Director of Products – Standards, Samsung
As the need for high-speed data storage and memory solutions continues to grow, developments in non-volatile storage protocols will continue to evolve faster than traditional storage protocols like SATA. When navigating these higher speed and lower latency protocols, you might be wondering, what the difference is between NVM Express® (NVMe®) technology and NAND? NVMe technology is not a competitor to NAND. In fact, NVMe technology provides an interface and protocol that fully unleashes the power of NAND. In this blog, we’ll look at how NVMe architecture works with NAND and provide clarity for those who have questions about “NVMe vs. NAND”.
What is NVMe Technology?
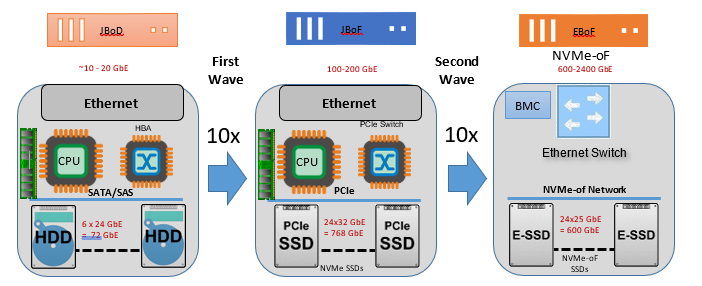
NVMe technology defines how host software communicates with non-volatile memory across multiple transports like a PCI Express® (PCIe®), RDMA, TCP and more. It is the industry standard for solid state drives (SSDs) in all form factors. In a first wave, A solid-state drive (SSD) using NVMe over PCIe® removes older protocol bottlenecks that were defined for hard disk drives (HDDs) and unleashes significant growth in data transfer rates and IOPS performance over other interfaces supporting SSDs such as SATA.
What is NAND?
NAND is a type of flash memory that reduces erase and write times lower than hard drive, and requires less chip area per cell, which allows for more storage density and lower cost. New 3D NAND technology is increasing performance, growing capacity and raising power efficiency of SSDs. 3D NAND stacks memory cells on top of each other, as opposed to 2D, which has a singular layer of cells. Along with PCIe and NVMe architectures, NAND is also able to support new applications that demand this higher physical layer storage interface performance. NAND technology can be found in SSDs and most commonly in smartphones.
NVMe and NAND: How Do These Technologies Work Together?
In the second wave, The NVM Express 2.0 library of specifications further exposes the power of NAND by defining and standardizing the various efficient I/O Command Sets specifications, including the NVM, Zoned Namespace and Key Value command sets. As NVMe technology evolves, NVMe-oF Ethernet-SSDs will further remove other system level bottlenecks to bring the NAND performance out to the servers where applications are running.
There are many benefits to NAND based NVMe SSDs. They contain the ability to support a mixture of form factors across the industry from M.2, U.2/2.5” and EDSFF. These SSDs also provide the support for PCs, gaming, data centers and Enterprise businesses.
Learn More
The future is bright for both NVMe architecture and NAND. As both technologies evolve, there are more opportunities for faster performance and innovations from software developers. For more insights from NVM Express members and to learn more about NVMe technology, check out more NVM Express blogs. To learn more about Samsung, please visit our website.